gcsescience.com 28 gcsescience.com
What is Gas Chromatography?
Instrumental
Methods - Identifying Compounds.
In gas chromatography
a small sample of a mixture
of compounds
is vapourised
(turned into gas).
A carrier gas takes the sample through the column.
The carrier gas (often nitrogen)
must
be inert and not
react with the sample.
The column is packed
with a solid material
which
slows the sample down.
Different compounds
travel
through the column at different
speeds and leave
the other end of the column at different
times. The
amount of time
a particular compound takes to pass
through
the instrument is called its retention time.
The retention time can help identify
the compound.
A recorder draws a graph
called a gas chromatogram
which shows a peak for each
compound.
The number of peaks
show the number of compounds
present in the sample and the position of the peaks
show the retention time. See the example
shown below.

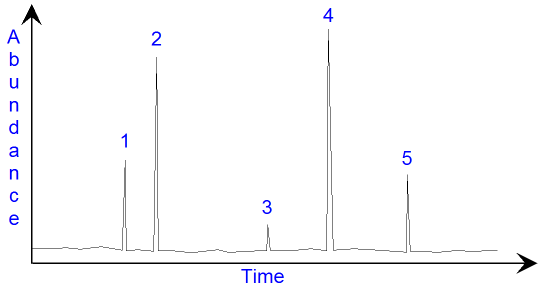
In the gas
chromatogram above, there are five peaks
showing that there are five compounds present. The
height of the peak
shows how much of the compound
there is in the mixture. A more accurate way
of identifying the different compounds
which leave the
column
can be made by using a mass
spectrometer.
See also paper chromatography.
![]() Links
Water
Revision Questions
Links
Water
Revision Questions
![]()
gcsescience.com The Periodic Table Index Water Quiz gcsescience.com
Home GCSE Chemistry GCSE Physics
Copyright © 2015 gcsescience.com. All Rights Reserved.